IS-IS Lab 3 Designated Router
Previous Next
Download Lab: VIRL | EVE-NG | GNS3
Image requirements:
Cisco IOSv (vios-adventerprisek9-m.vmdk.SPA.156-2.T)
Introduction:
This is a small lab but very powerful, here you will learn about IS-IS routers in the broadcast networks, mainly you will identify which node is the designated router and then modify IS-IS interface priority to control DIS election process.
Nodes Access:
Enable: cisco
Username: cisco
Password: cisco
Lab goals:
1. Determine which router is the DIS for each IS-IS Area.
2. Understand that there could be 2 designated routers in one area, one for level-1 and another for level-2 IS-type. Identify if the same node in the area acts as DIS for both L1 and L2.
3. Change the designated router for L1 in both areas to any other router than the current one by modifying the IS-IS interface priority. Bigger is more preferable, the range is 0 to 127.
4. Change the designated router for L2 in both areas to any other router than the current one by modifying the IS-IS interface priority. Bigger is more preferable, the range is 0 to 127.
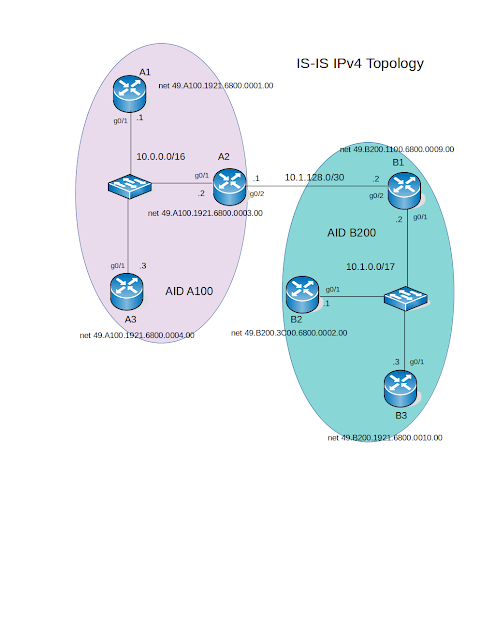
Topology:
Get Started:
Note: I used VIRL while writing this lab, if you will use EVE-NG or GNS3 in your topology, you will have probably different MAC addresses for interfaces and that is why default Designates Router for broadcast domains will be rather something else than what I had, default IS-IS interface priority is 64 so it uses higher MAC address to choose who will be a DIS, so while you do this lab just use information from your show command output instead of what I have here.
Step1: The command you need to use for objective one is "show isis neighbors", it will reveal valuable information about the neighbors' state. Let's examine neighbor table on the router A1:
A1#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id A2 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.2 UP 8 A2.01
A2 L2 Gi0/1 10.0.0.2 UP 8 A2.01
A3 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.3 UP 26 A2.01
A3 L2 Gi0/1 10.0.0.3 UP 25 A2.01
From the output, you can see that router A1 has two neighbors routers A2 and A3 and per each neighbor, there is adjacency for is-type L1 and L2. The Circuit-Id column shows important parameters, for each line of output the A2.01 indicates that the router A2 is the Designated IS on this LAN for Area A100 and level-1 and level-2.
Next, examine the area B200, will choose router B1:
B1#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
A2 L2 Gi0/2 10.1.128.1 UP 21 B1.02
B3 L1 Gi0/1 10.1.0.3 UP 21 B2.01
B3 L2 Gi0/1 10.1.0.3 UP 29 B2.01
B2 L1 Gi0/1 10.1.0.1 UP 9 B2.01
B2 L2 Gi0/1 10.1.0.1 UP 8 B2.01
From the Circuit-Id column, you can derive that Router B2 is the DIS in this broadcast domain for the Area B200. Also, the link between routers A2 and B1 does not belong to any particular area but it is like the border between areas A100 and B200, instead of the router like in OSPF, IS-IS border falls onto the "Link". This Link is broadcast domain on its own and B1 is the DIS for it.
Step2: Regarding the lab's goal number two, the output of the IS-IS neighbor table shows that there is only one router acting as DIS for both IS-types, in Area A100 this is router A2 and in the Area B200 is router B2.
Step3 and 4: To complete these Lab goals, you are going to configure router A1 as DIS for L1 and Router A3 as DIS for L2 in the Area A100. The same goes for Area B200, router B1 is DIS for L1 and router B3 is DIS for L2 after you complete IS-IS interface priority modification verify if the desired result has been achieved. IS-IS interface priority is 100.
Configuration example:
!
A1(config)#interface g0/1
A1(config-if)#isis priority 100 level-1
!
!
A3(config)#interface g0/1
A3(config-if)#isis priority 100 level-2
Save running-config then verify if results are changed from router A2 point of view:
A2#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
B1 L2 Gi0/2 10.1.128.2 UP 24 A2.02
A1 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.1 UP 8 A1.01
A1 L2 Gi0/1 10.0.0.1 UP 26 A3.01
A3 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.3 UP 26 A1.01
A3 L2 Gi0/1 10.0.0.3 UP 6 A3.01
As you can see, you achieved what is intended to be, router A1 is the DIS for L1 IS-type and router A3 is the DIS for L2.
Finish this lab by completing the same steps for Area B200.
This command also come in handy when verifying IS-IS parameters:
B2#show clns interface g0/1
Summary:
IS-IS elect only one DIS per LAN if the new router with higher priority will be introduced to a topology it will automatically take over the role of the current designated router.
Download Lab: VIRL | EVE-NG | GNS3
Image requirements:
Cisco IOSv (vios-adventerprisek9-m.vmdk.SPA.156-2.T)
Introduction:
This is a small lab but very powerful, here you will learn about IS-IS routers in the broadcast networks, mainly you will identify which node is the designated router and then modify IS-IS interface priority to control DIS election process.
Nodes Access:
Enable: cisco
Username: cisco
Password: cisco
Lab goals:
1. Determine which router is the DIS for each IS-IS Area.
2. Understand that there could be 2 designated routers in one area, one for level-1 and another for level-2 IS-type. Identify if the same node in the area acts as DIS for both L1 and L2.
3. Change the designated router for L1 in both areas to any other router than the current one by modifying the IS-IS interface priority. Bigger is more preferable, the range is 0 to 127.
4. Change the designated router for L2 in both areas to any other router than the current one by modifying the IS-IS interface priority. Bigger is more preferable, the range is 0 to 127.
Topology:
Get Started:
Note: I used VIRL while writing this lab, if you will use EVE-NG or GNS3 in your topology, you will have probably different MAC addresses for interfaces and that is why default Designates Router for broadcast domains will be rather something else than what I had, default IS-IS interface priority is 64 so it uses higher MAC address to choose who will be a DIS, so while you do this lab just use information from your show command output instead of what I have here.
Step1: The command you need to use for objective one is "show isis neighbors", it will reveal valuable information about the neighbors' state. Let's examine neighbor table on the router A1:
A1#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id A2 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.2 UP 8 A2.01
A2 L2 Gi0/1 10.0.0.2 UP 8 A2.01
A3 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.3 UP 26 A2.01
A3 L2 Gi0/1 10.0.0.3 UP 25 A2.01
From the output, you can see that router A1 has two neighbors routers A2 and A3 and per each neighbor, there is adjacency for is-type L1 and L2. The Circuit-Id column shows important parameters, for each line of output the A2.01 indicates that the router A2 is the Designated IS on this LAN for Area A100 and level-1 and level-2.
Next, examine the area B200, will choose router B1:
B1#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
A2 L2 Gi0/2 10.1.128.1 UP 21 B1.02
B3 L1 Gi0/1 10.1.0.3 UP 21 B2.01
B3 L2 Gi0/1 10.1.0.3 UP 29 B2.01
B2 L1 Gi0/1 10.1.0.1 UP 9 B2.01
B2 L2 Gi0/1 10.1.0.1 UP 8 B2.01
From the Circuit-Id column, you can derive that Router B2 is the DIS in this broadcast domain for the Area B200. Also, the link between routers A2 and B1 does not belong to any particular area but it is like the border between areas A100 and B200, instead of the router like in OSPF, IS-IS border falls onto the "Link". This Link is broadcast domain on its own and B1 is the DIS for it.
Step2: Regarding the lab's goal number two, the output of the IS-IS neighbor table shows that there is only one router acting as DIS for both IS-types, in Area A100 this is router A2 and in the Area B200 is router B2.
Step3 and 4: To complete these Lab goals, you are going to configure router A1 as DIS for L1 and Router A3 as DIS for L2 in the Area A100. The same goes for Area B200, router B1 is DIS for L1 and router B3 is DIS for L2 after you complete IS-IS interface priority modification verify if the desired result has been achieved. IS-IS interface priority is 100.
Configuration example:
!
A1(config)#interface g0/1
A1(config-if)#isis priority 100 level-1
!
!
A3(config)#interface g0/1
A3(config-if)#isis priority 100 level-2
Save running-config then verify if results are changed from router A2 point of view:
A2#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
B1 L2 Gi0/2 10.1.128.2 UP 24 A2.02
A1 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.1 UP 8 A1.01
A1 L2 Gi0/1 10.0.0.1 UP 26 A3.01
A3 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.3 UP 26 A1.01
A3 L2 Gi0/1 10.0.0.3 UP 6 A3.01
As you can see, you achieved what is intended to be, router A1 is the DIS for L1 IS-type and router A3 is the DIS for L2.
Finish this lab by completing the same steps for Area B200.
This command also come in handy when verifying IS-IS parameters:
B2#show clns interface g0/1
Summary:
IS-IS elect only one DIS per LAN if the new router with higher priority will be introduced to a topology it will automatically take over the role of the current designated router.
Comments
Post a Comment