IS-IS Lab 16 Troubleshooting Multi-Area Solution
Download Lab: VIRL | EVE-NG | GNS3
Image requirements:
Cisco IOSv (vios-adventerprisek9-m.vmdk.SPA.156-2.T)
Introduction:
This is the solution lab for troubleshooting scenario described in the IS-IS lab 15th, here step by step, an explanation will be given on how to fix the connectivity issues encountered after reconfiguring one L2 area topology into multiple areas. Some subnets are no longer able to reach each other due to improper configuration of IS-IS protocol. Let's dive into the problem resolution.
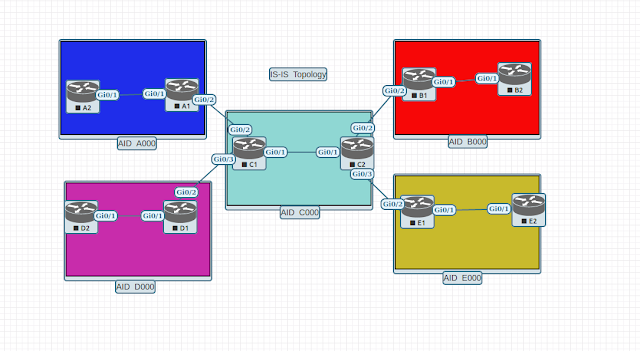
Topology:
Reported issues:
1. Router A2 unable to ping any IP addresses assigned to loopback 0 interfaces in the topology if sourced from its own loopback 0 interface.
2. Router B2 unable to ping any IP addresses assigned to loopback 0 interfaces in the topology if sourced from its own loopback 0 interface.
3. Router D2 unable to ping any IP addresses assigned to loopback 0 interfaces in the topology if sourced from its own loopback 0 interface.
4. Router E2 unable to ping any IP addresses assigned to loopback 0 interfaces in the topology if sourced from its own loopback 0 interface.
Solution:
Step1: It would be nice to confirm the reported issue first before you start identifying the cause of the problem. Issue number 1 states that router A2 unable to ping any IP address of loopback 0 interfaces in the topology, so let's verify that by pinging a couple of remote addresses.
On router A2 source ping from its loopback0 interface to the router E2 and router C2:
A2#ping 192.168.0.7 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.7, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
A2#ping 192.168.0.8 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.8, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
The results of the output indicate that ping requests are timing out.
Step2: Draw the initial hypophysis from gathered information of the ping results. If there would be a problem at the remote location when next-hop of router A2 would potentially send back destination unreachable message but since the ping is timing out, there could be a problem for next-hop router reach back the IP address of loopback0 of router A2. Gather addition information by pinging IP address of router A1 on the link between A1 and A2.
Identify the IP address of router A1 on the interface facing router A2:
A1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 10.255.1.41 YES TFTP up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 10.0.0.25 YES TFTP up up
GigabitEthernet0/2 10.0.0.9 YES TFTP up up
Loopback0 192.168.0.2 YES TFTP up up
According to the diagram interface on the router A1 facing router A2 is G0/1.
From the output, this interface has IP address of 10.0.0.25.
A2#ping 10.0.0.25
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.25, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 2/2/3 ms
A2#
Ping sourced from the G0/1 interface on the router A2 shows that there is L3 connectivity between two routers. Now let's see if ping from the loopback0 interface will work.
A2#ping 10.0.0.25 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.25, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
A2#
The result of the ping command indicates that router A1 unable to respond to the ICMP request messages.
Step3: Gather more information, routers A1 and A2 are both in the IS-IS L1 Area with AID of A000. Verify if IS-IS neighborship is formed between these two routers.
A2#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
A1 L1 Gi0/1 10.0.0.25 UP 8 A1.01
The output shows that L1 adjacency is formed, so neighborship issues can be eliminated. Next would a good idea to check what is in the IS-IS database.
A2#show isis database
IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime/Rcvd ATT/P/OL
A1.00-00 0x00000006 0xB9B6 1071/1199 1/0/0
A1.01-00 0x00000003 0x016D 600/1199 0/0/0
A2.00-00 * 0x00000004 0xDB9D 504/* 0/0/0
There are three LSPs in the database. First LSP belongs to the router A1 and its LSP carrying prefixes, also it indicates that router A1 is an L1/L2 border router and A2 has to have the default route installed in RIB because ATT bit set to 1.
The second LSP indicates that router A1 is the DIS on the link between A1 and A2 because pseudonode-ID is set to nonzero.
Last LSP belongs to router A2, it contains prefixes router will advertise to its neighbors. Examining the detailed database for this LSP will give insights on what could be a problem.
A2#show isis database detail A2.00-00
IS-IS Level-1 LSP A2.00-00
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime/Rcvd ATT/P/OL
A2.00-00 * 0x00000006 0xD79F 1120/* 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.a000
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: A2
Metric: 10 IS A1.01
IP Address: 10.0.0.26
Metric: 10 IP 10.0.0.24 255.255.255.252
A2#
Router A2 does not have in its LSP IP information regarding the loopback0 interface.
Step4: Now it's good to see if the loopback0 interface is enabled for IS-IS protocol.
A2#show running-config interface lo0Building configuration...
Current configuration : 175 bytes
!
interface Loopback0
description Loopback
ip address 192.168.0.10 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:B:0:1::3/128
isis circuit-type level-2-only
The output clearly shows that IS-IS protocol is enabled but it also reveals something else, the circuit-type is set to be level-2-only.
But if review the isis protocol information:
A2#show isis protocol
IS-IS Router: <Null Tag>
System Id: 0000.0000.00A2.00 IS-Type: level-1
Manual area address(es):
49.a000
Routing for area address(es):
49.a000
Interfaces supported by IS-IS:
GigabitEthernet0/1 - IP
Loopback0 - IP
Redistribute:
static (on by default)
Distance for L2 CLNS routes: 110
RRR level: none
Generate narrow metrics: level-1-2
Accept narrow metrics: level-1-2
Generate wide metrics: none
Accept wide metrics: none
This router is set to be IS-Type Level-1, meaning that it will not include any L2 information in its database. L2 information will not be communicated over the link as well since the interface set to be circuit-type level-1.
A2#show clns interface g0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Checksums enabled, MTU 1497, Encapsulation SAP
ERPDUs enabled, min. interval 10 msec.
CLNS fast switching disabled
CLNS SSE switching disabled
DEC compatibility mode OFF for this interface
Next ESH/ISH in 46 seconds
Routing Protocol: IS-IS
Circuit Type: level-1
Interface number 0x1, local circuit ID 0x1
Level-1 Metric: 10, Priority: 64, Circuit ID: A1.01
DR ID: A1.01
Level-1 IPv6 Metric: 10
Number of active level-1 adjacencies: 1
Next IS-IS LAN Level-1 Hello in 7 seconds
Step5: Adequate amount of information has been collected to propose a solid hypophysis on the problem-solution. Since routers, A1 and A2 are IS-IS neighbors via the L1 adjacency and router A2 is enabled as L1 IS-type only, the L1 database is only supported on the A2 node. Configuring loopback0 as circuit-type level-2-only will disqualify this interface from participating in the IS-IS routing process.
Step6: Implement the solution. Change the circuit-type of node A2's interface to level-1.
A2(config)#interface lo0
A2(config-if)#isis circuit-type level-1
A2(config-if)# end
Step7: Verify the implemented solution:
A2#show clns interface lo0Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up
Checksums enabled, MTU 1514, Encapsulation LOOPBACK
ERPDUs enabled, min. interval 10 msec.
CLNS fast switching disabled
CLNS SSE switching disabled
DEC compatibility mode OFF for this interface
Next ESH/ISH in 24 seconds
Routing Protocol: IS-IS
Circuit Type: level-1
Interface number 0x0, local circuit ID 0x100
Level-1 Metric: 10, Priority: 64, Circuit ID: A2.00
Level-1 IPv6 Metric: 10
Number of active level-1 adjacencies: 0
Next IS-IS Hello in 0 seconds
if state DOWN
This output shows that circuit-type has been changed to level-1.
A2#show isis database detail A2.00-00
IS-IS Level-1 LSP A2.00-00
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime/Rcvd ATT/P/OL
A2.00-00 * 0x00000009 0xFC1D 1019/* 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.a000
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: A2
Metric: 10 IS A1.01
IP Address: 192.168.0.10
Metric: 10 IP 10.0.0.24 255.255.255.252
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.0.10 255.255.255.255
Now router A2's LSP contains the prefix of the loopback0 interface. Let's see if ping to some remote destinations will be successful.
A2#ping 10.0.0.25 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.25, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 2/2/5 ms
A2#
Ping to router A1's interface G0/1 is good. Next, verify connectivity to the core router C2.
A2#ping 192.168.0.8 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.8, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
!!!!!
Router A2 is able to communicate with core router C2. Now, can it ping the loopback0 interfaces of routers B2, D2, and E2?
A2#ping 192.168.0.6 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
A2#ping 192.168.0.9 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.9, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
A2#ping 192.168.0.7 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.7, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
As results in the output indicate that ping failed to reach all three routers, further troubleshooting is necessary.
Step8: Let's go to the router B2 and check what is going on with that node. A lot of effort put into fixing A2's reachability issues and experience obtained from the time spent on resolving the problem allows you to assume that router B2 might have the same issue. Go straight and verify the database on the router B2.
B2#show isis database detail B2.00-00
IS-IS Level-1 LSP B2.00-00
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime/Rcvd ATT/P/OL
B2.00-00 * 0x0000000A 0xFB56 332/* 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.b000
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: B2
Metric: 10 IS B1.01
IP Address: 10.0.0.18
Metric: 10 IP 10.0.0.16 255.255.255.252
The output indicates that the loopback0 interface's IP address is not in the LSP for router B2. Check the circuit-type of lo0 and IS-IS protocol.
B2#show clns interface lo0
Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up
Checksums enabled, MTU 1514, Encapsulation LOOPBACK
ERPDUs enabled, min. interval 10 msec.
CLNS fast switching disabled
CLNS SSE switching disabled
DEC compatibility mode OFF for this interface
Next ESH/ISH in 27 seconds
Routing Protocol: IS-IS
Circuit Type: level-2
Interface number 0x0, local circuit ID 0x100
Next IS-IS Hello in 0 seconds
if state DOWN
B2#show isis protocol
IS-IS Router: <Null Tag>
System Id: 0000.0000.00B2.00 IS-Type: level-1
Manual area address(es):
49.b000
Routing for area address(es):
49.b000
Interfaces supported by IS-IS:
GigabitEthernet0/1 - IP
Loopback0 - IP
Redistribute:
static (on by default)
Distance for L2 CLNS routes: 110
RRR level: none
Generate narrow metrics: level-1-2
Accept narrow metrics: level-1-2
Generate wide metrics: none
Accept wide metrics: none
Indeed, node B2 has the same problem as router A2.
Step9: Change circuit-type for B2's loopback0 interface.
B2(config)#interface lo0
B2(config-if)#isis circuit-type level-1
Step10: Verify solution and connectivity.
B2#show isis database detail B2.00-00
IS-IS Level-1 LSP B2.00-00
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime/Rcvd ATT/P/OL
B2.00-00 * 0x0000000C 0xCA2B 1116/* 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.b000
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: B2
Metric: 10 IS B1.01
IP Address: 192.168.0.6
Metric: 10 IP 10.0.0.16 255.255.255.252
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.0.6 255.255.255.255
B2#ping 192.168.0.10 source lo0Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.6
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 6/7/9 ms
B2#
Ping to the router A2's loopback0 interface is successful.
B2#ping 192.168.0.9 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.9, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.6
U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
B2#ping 192.168.0.7 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.7, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.6
U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
B2#
Well, routers D2 and E2 are still unavailable but the problem might be the same to fix this.
Step11: Verify D2's and E2's loopback0 interfaces' circuit-type:
D2#show clns interface lo0
Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up
Checksums enabled, MTU 1514, Encapsulation LOOPBACK
ERPDUs enabled, min. interval 10 msec.
CLNS fast switching disabled
CLNS SSE switching disabled
DEC compatibility mode OFF for this interface
Next ESH/ISH in 11 seconds
Routing Protocol: IS-IS
Circuit Type: level-2
Interface number 0x0, local circuit ID 0x100
Next IS-IS Hello in 0 seconds
if state DOWN
E2#show clns interface lo0
Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up
Checksums enabled, MTU 1514, Encapsulation LOOPBACK
ERPDUs enabled, min. interval 10 msec.
CLNS fast switching disabled
CLNS SSE switching disabled
DEC compatibility mode OFF for this interface
Next ESH/ISH in 4 seconds
Routing Protocol: IS-IS
Circuit Type: level-2
Interface number 0x0, local circuit ID 0x100
Next IS-IS Hello in 0 seconds
if state DOWN
Both of these interfaces have circuit-type of level-2 which is incorrect.
Step12: Change circuit-type for D2's and E2's loopback0 interfaces.
D2(config)#interface lo0
D2(config-if)#isis circuit-type level-1
!
E2(config)#interface lo0
E2(config-if)#isis circuit-type level-1
Step13: Assuming that changes in the previous step, finally fix all issues related to the connectivity, now verify that router A2 is able to ping loopback0 addresses fo B2, D2, and E3.
A2#ping 192.168.0.6 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 7/7/9 ms
A2#ping 192.168.0.9 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.9, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/5/10 ms
A2#ping 192.168.0.7 source lo0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.7, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.0.10
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 7/7/9 ms
A2#

Comments
Post a Comment